What is Six Sigma?
As per Jack welch “Six Sigma is a quality program that, when all is said and done, improves your customer’s experience, lowers your costs, and builds better leaders.”
Six Sigma is simply a method of efficiently solving a problem. Using Six Sigma reduces the amount of defective products manufactured or services provided, resulting in increased revenue and greater customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma is a method that provides organizations tools to improve the capability of their business processes.
This increase in performance and decrease in process variation lead to defect reduction and improvement in profits, employee morale, and quality of products or services.
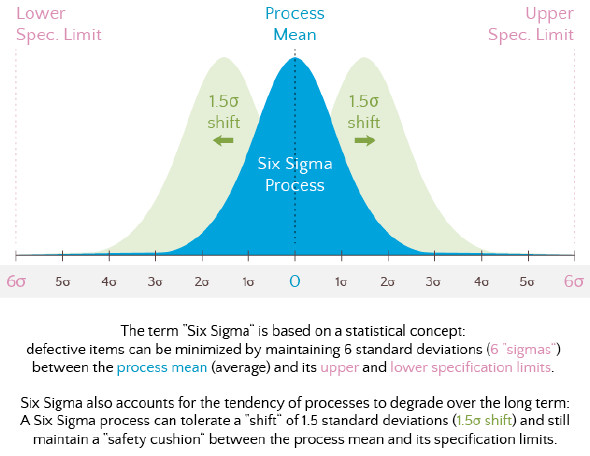
Six Sigma quality is a term generally used to indicate a process is well controlled (within process limits ±3s from the center line in a control chart, and requirements/tolerance limits ±6s from the center line).
Different definitions have been proposed for Six Sigma, but they all share some common threads:
Use of teams that are assigned well-defined projects that have direct impact on the organization’s bottom line.
Training in “statistical thinking” at all levels and providing key people with extensive training in advanced statistics and project management.
These key people are designated “Black Belts.” Review the different Six Sigma belts, levels and roles.
Emphasis on the DMAIC approach to problem solving: define, measure, analyze, improve, and control.
A management environment that supports these initiatives as a business strategy.
Six Sigma offers six major benefits that attract companies:
Generates sustained success
Sets a performance goal for everyone
Enhances value to customers
Accelerates the rate of improvement
Promotes learning and cross-pollination
Executes strategic change
What exactly does “Six Sigma” mean?
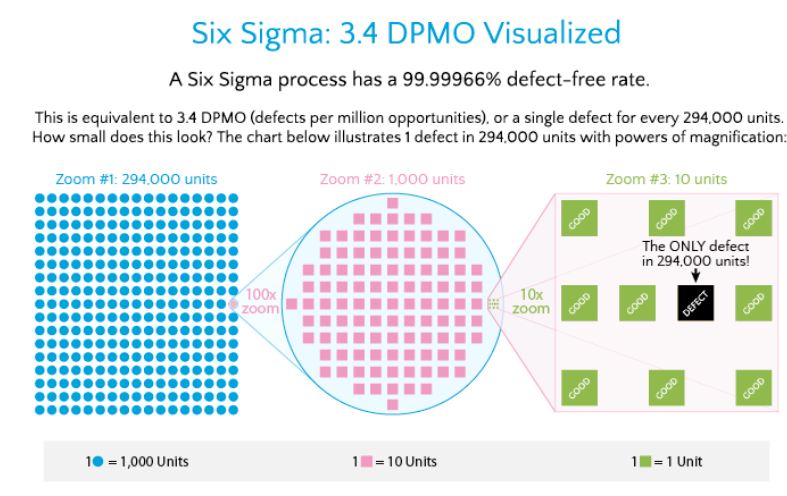
Six Sigma is named after a statistical concept where a process only produces 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO). Six Sigma can therefore be also thought of as a goal, where processes not only encounter less defects, but do so consistently (low variability).
Basically, Six Sigma reduces variation, so products or services can be delivered as expected reliably.
Six sigma: Statistically visualized
Differing opinions on the definition of Six Sigma:
Philosophy — The philosophical perspective views all work as processes that can be defined, measured, analyzed, improved and controlled.
Processes require inputs (x) and produce outputs (y). If you control the inputs, you will control the outputs.
This is generally expressed as y = f(x).
Set of tools — The Six Sigma expert uses qualitative and quantitative techniques to drive process improvement.
A few such tools include statistical process control (SPC), control charts, failure mode and effects analysis, and process mapping. Six Sigma professionals do not totally agree as to exactly which tools constitute the set.
Methodology — This view of Six Sigma recognizes the underlying and rigorous approach known as DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve and control).
DMAIC defines the steps a Six Sigma practitioner is expected to follow, starting with identifying the problem and ending with the implementation of long-lasting solutions.
While DMAIC is not the only Six Sigma methodology in use, it is certainly the most widely adopted and recognized.
Metrics – In simple terms, Six Sigma quality performance means 3.4 defects per million opportunities (accounting for a 1.5-sigma shift in the mean).
Features of Six Sigma
Six Sigma’s aim is to eliminate waste and inefficiency, thereby increasing customer satisfaction by delivering what the customer is expecting.
Six Sigma follows a structured methodology, and has defined roles for the participants.
Six Sigma is a data driven methodology, and requires accurate data collection for the processes being analyzed.
Six Sigma is about putting results on Financial Statements.
Six Sigma is a business-driven, multi-dimensional structured approach for:
Improving Processes
Lowering Defects
Reducing process variability
Reducing costs
Increasing customer satisfaction
Increased profits
The word Sigma is a statistical term that measures how far a given process deviates from perfection.
The central idea behind Six Sigma:
If you can measure how many “defects” you have in a process, you can systematically figure out how to eliminate them and get as close to “zero defects” as possible and specifically it means a failure rate of 3.4 parts per million or 99.9997% perfect.
The statistical representation of Six Sigma describes quantitatively how a process is performing.
To achieve Six Sigma, a process must not produce more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
A Six Sigma defect is defined as anything outside of customer specifications.
A Six Sigma opportunity is then the total quantity of chances for a defect.
Process sigma can easily be calculated using a Six Sigma calculator.
The fundamental objective of the Six Sigma methodology is the implementation of a measurement-based strategy that focuses on process improvement and variation reduction through the application of Six Sigma improvement projects.
This is accomplished through the use of two Six Sigma sub-methodologies: DMAIC and DMADV.
The Six Sigma DMAIC process (define, measure, analyze, improve, control) is an improvement system for existing processes falling below specification and looking for incremental improvement.
The Six Sigma DMADV process (define, measure, analyze, design, verify) is an improvement system used to develop new processes or products at Six Sigma quality levels. It can also be employed if a current process requires more than just incremental improvement.
Both Six Sigma processes are executed by Six Sigma Green Belts and Six Sigma Black Belts, and are overseen by Six Sigma Master Black Belts.
According to the Six Sigma Academy, Black Belts save companies approximately $230,000 per project and can complete four to six projects per year. (Given that the average Black Belt salary is $80,000 in the United States, that is a fantastic return on investment.)
General Electric, one of the most successful companies implementing Six Sigma, has estimated benefits on the order of $10 billion during the first five years of implementation. GE first began Six Sigma in 1995 after Motorola and Allied Signal blazed the Six Sigma trail.
Since then, thousands of companies around the world have discovered the far reaching benefits of Six Sigma.
Many frameworks exist for implementing the Six Sigma methodology.
Six Sigma Consultants all over the world have developed proprietary methodologies for implementing Six Sigma quality, based on the similar change management philosophies and applications of tools.
